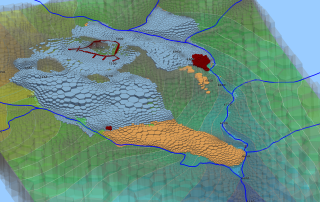
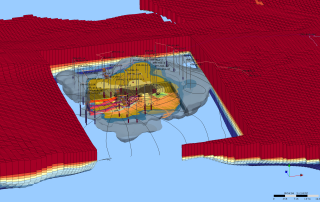
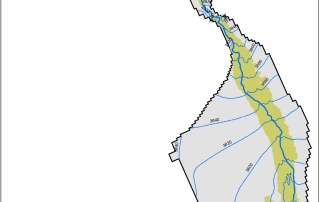
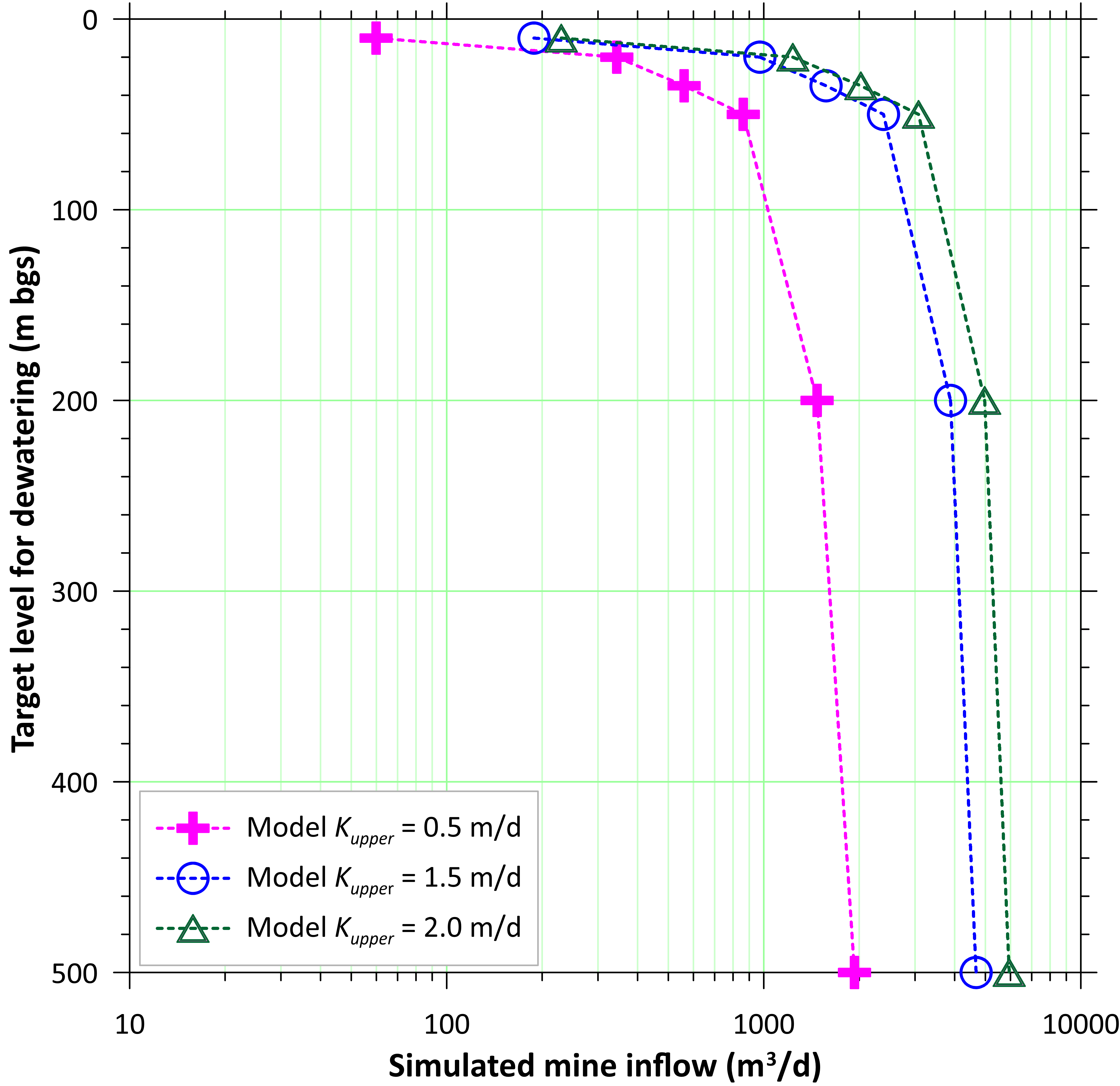
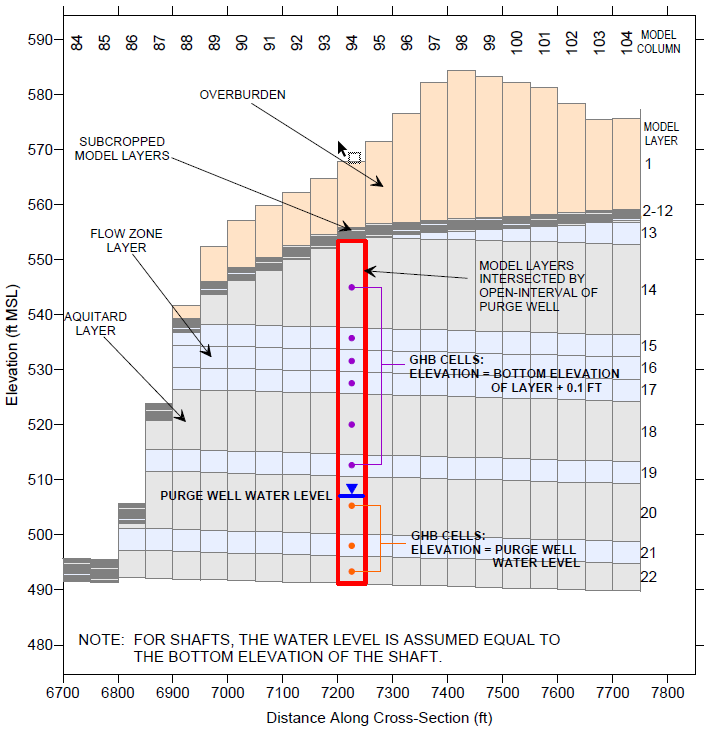
SSP&A is best known for our modeling and hydrogeology expertise. We provide these services alone or as components of larger, more complex projects, often combining our modeling services with our other core areas – for example, developing specialized methods, software and models.
SSP&A is often retained by other consultants to independently review or calibrate third-party models. Our ability to build, evaluate, and update comprehensive groundwater models combined with our expertise and understanding of hydrology, enables us to discern what is realistic and what is not, and produce deliverables that will stand up to scrutiny.
Hydrogeology
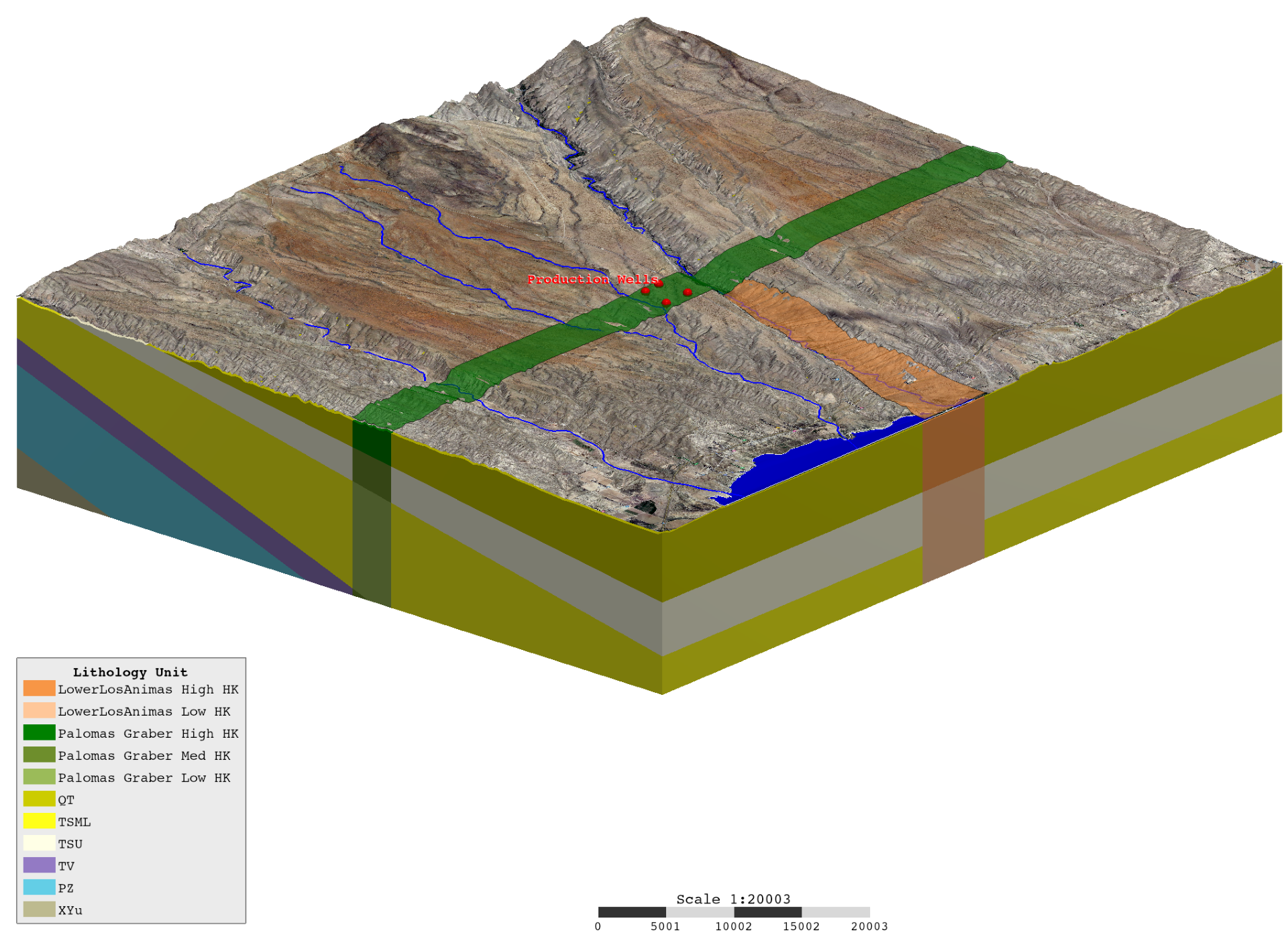
SSP&A’s hydrogeologists collaborate with their colleagues in our other discipline areas to develop hydrogeological conceptual models (HCMs) to underpin decision making; design and apply computational environmental models of groundwater, surface water, soil vapor and density-dependent conditions; and develop and implement engineering solutions when needed. Example services include:
- Analysis of aquifer tests, including the development and teaching of professional courses;
- Water supply safe and sustainable yield assessment;
- Surface water hydraulics and watershed delineation;
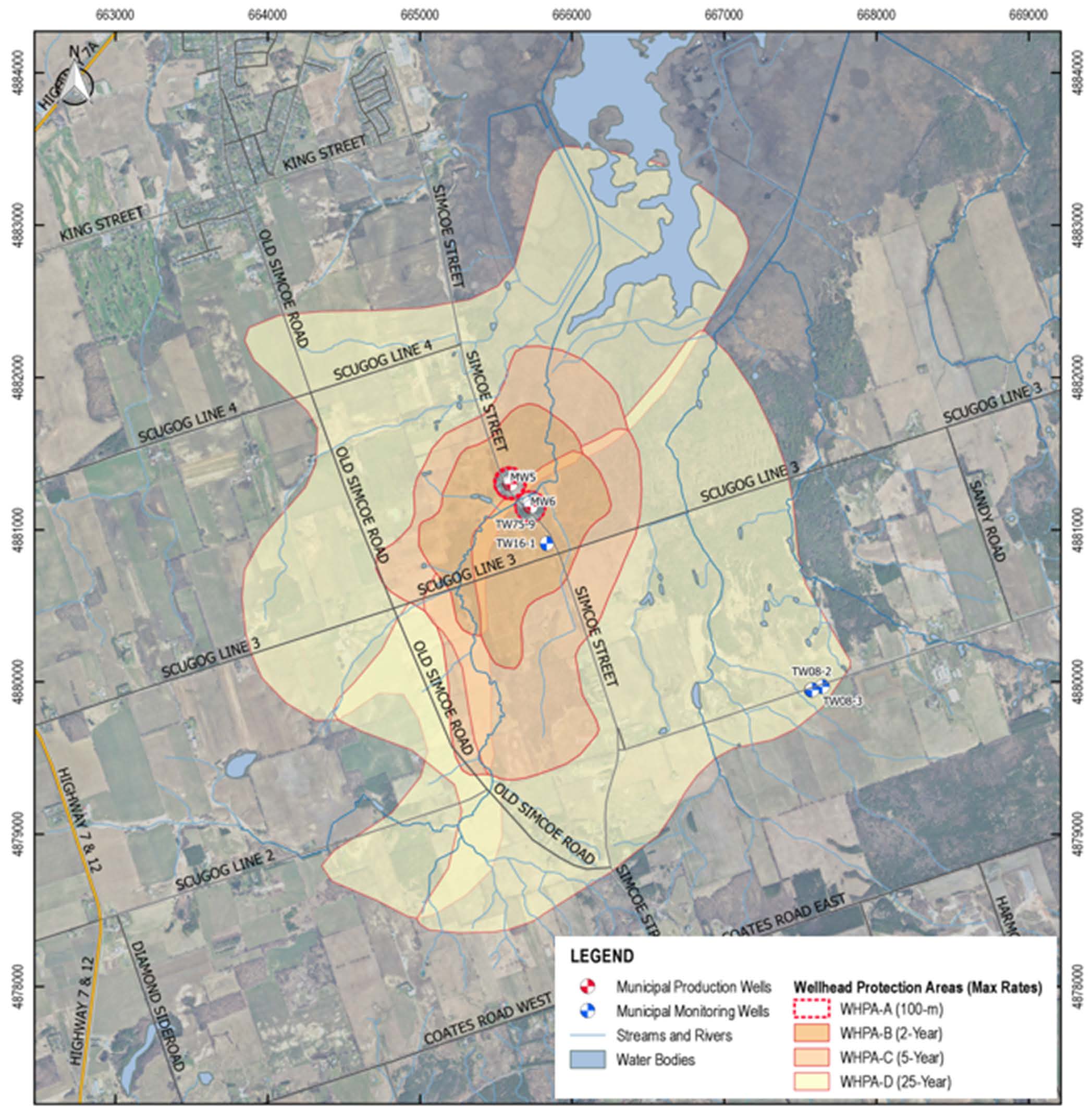
- Wellhead protection area delineation;
- Spring discharge analysis and sustainability determination;
- Managed aquifer recharge (MAR), and other infiltration studies;
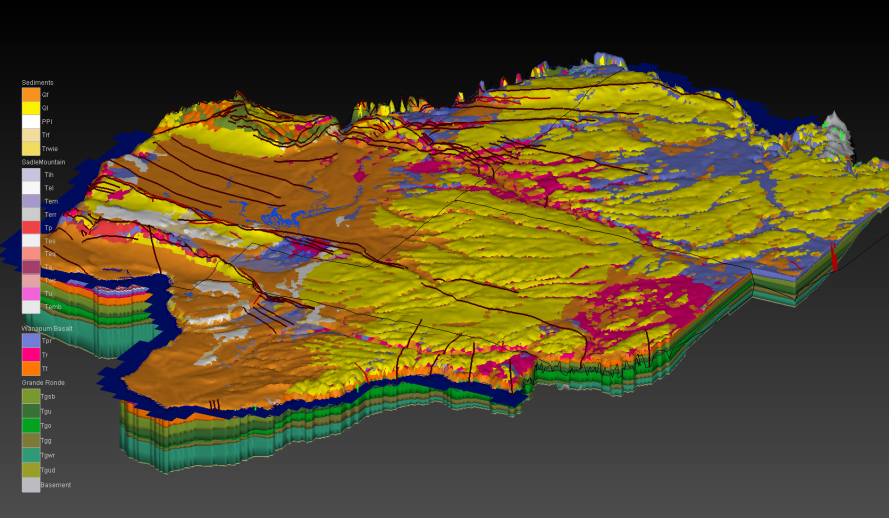
- Geological mapping and the development of geological and hydrogeological frameworks; and
- Fractured-rock aquifer characterization.
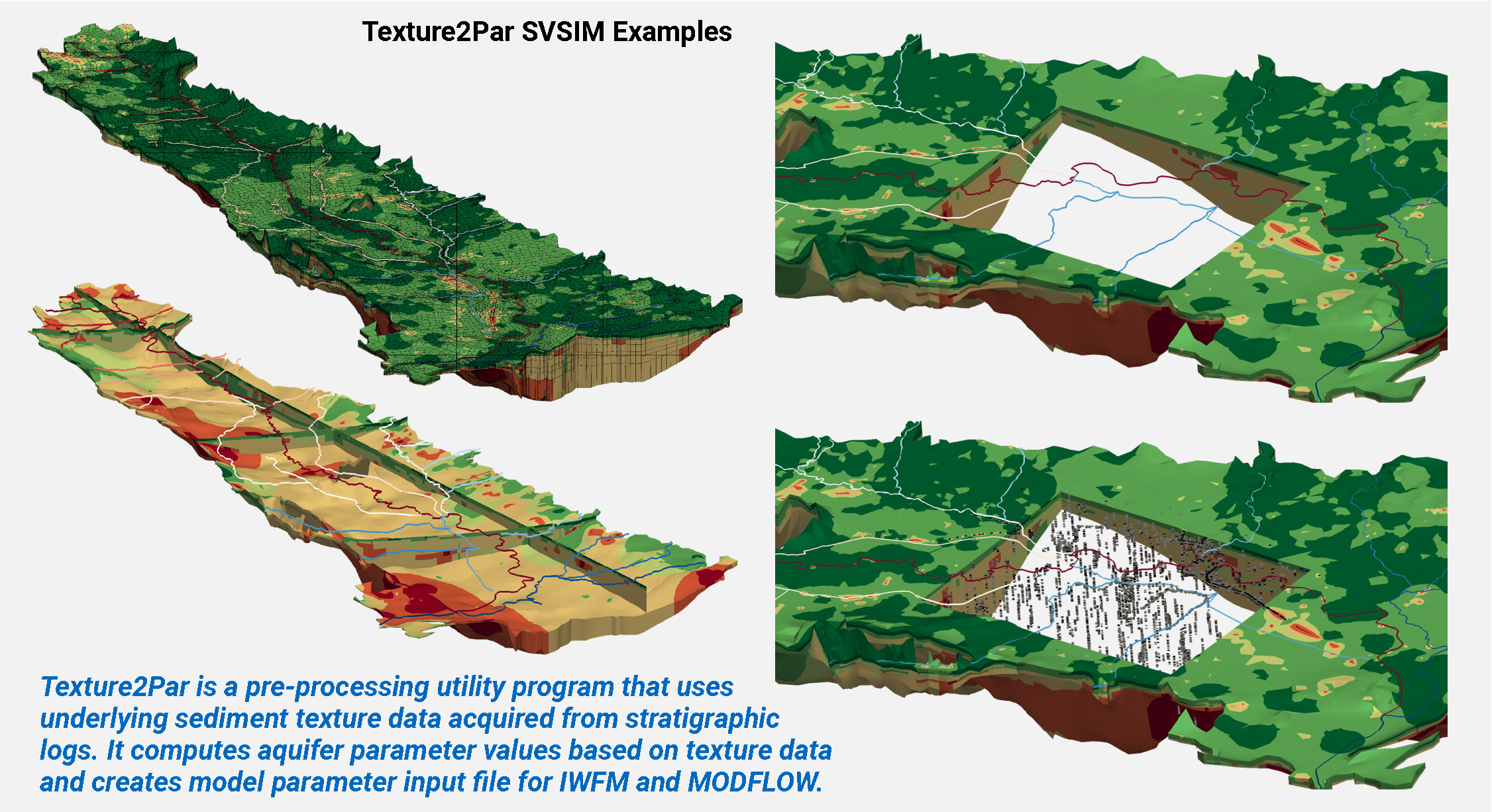
Our hydrogeologists use specialized geological data processing, visualization, and interpretation software including Rockworks, Leapfrog, EVS/MVS, and our own software developed in-house – GroundWater Desktop (GWD) – to specifically enable the integrated visualization of environmental data together with models constructed using those data.
SSP&A has in-house modeling software development capabilities, data management and analysis expertise, and a team of hydrogeologists, geochemists, engineers, scientists, and software developers.
Environmental Modeling
Multimedia environmental modeling is an SSP&A trademark – including groundwater-flow, solute-transport, variable saturation, density dependence, and land-surface processes. With decades of experience and theoretical method development; simulation code design, testing, and implementation; and model construction and application, we develop and apply a variety of simulation codes tailored to each specific project. This includes creating physics-based, statistical, and hybrid models to shed light on environmental issues; predict potential outcomes; and test hypotheses and evaluate and contrast solutions. Although many applications in our industry focus on water resource applications and contaminant fate and transport modeling for remediation and risk analysis, other applications include simulating underground storage tank leaks; vadose zone migration including soil vapor recovery; monitoring network design and optimization; and other use cases.
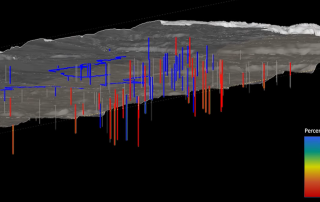
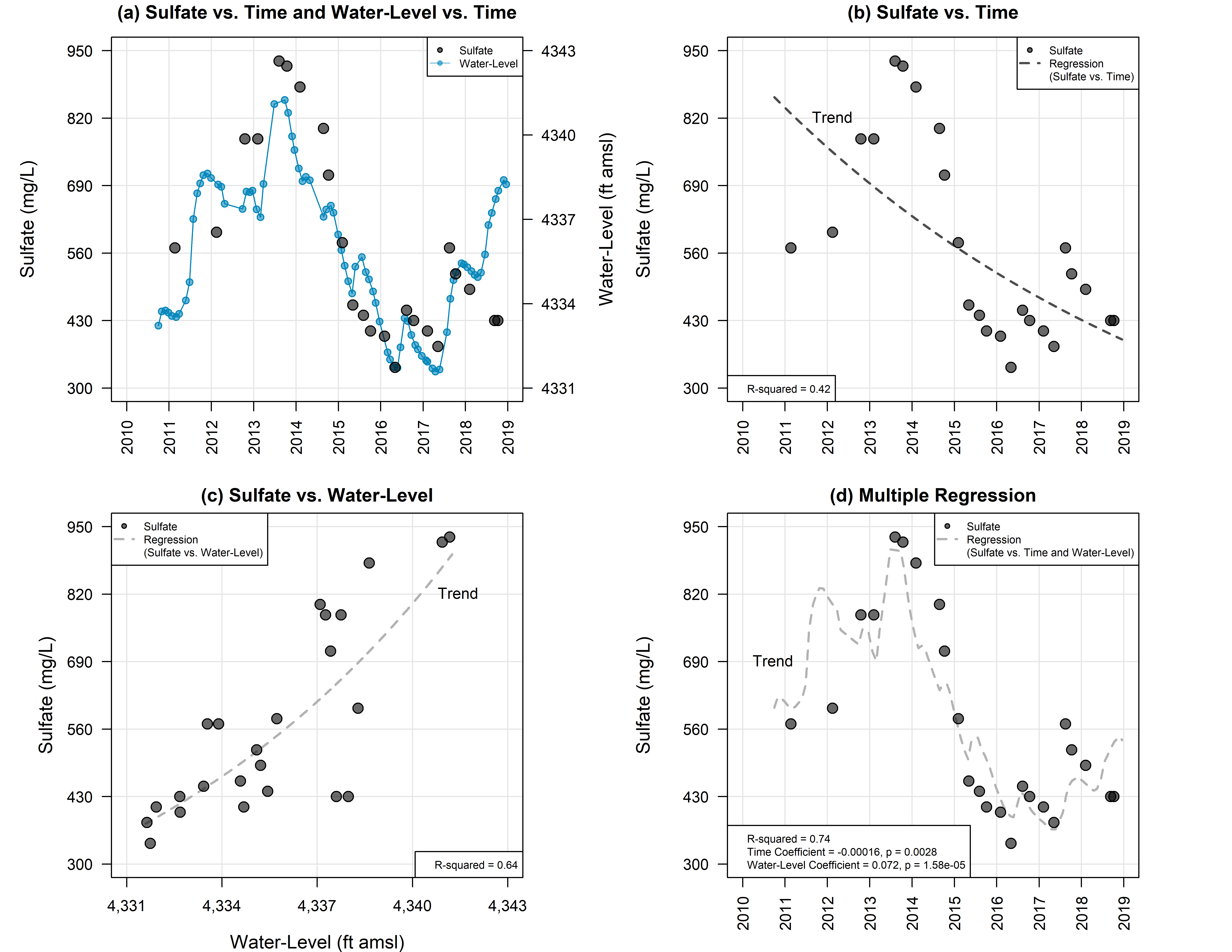
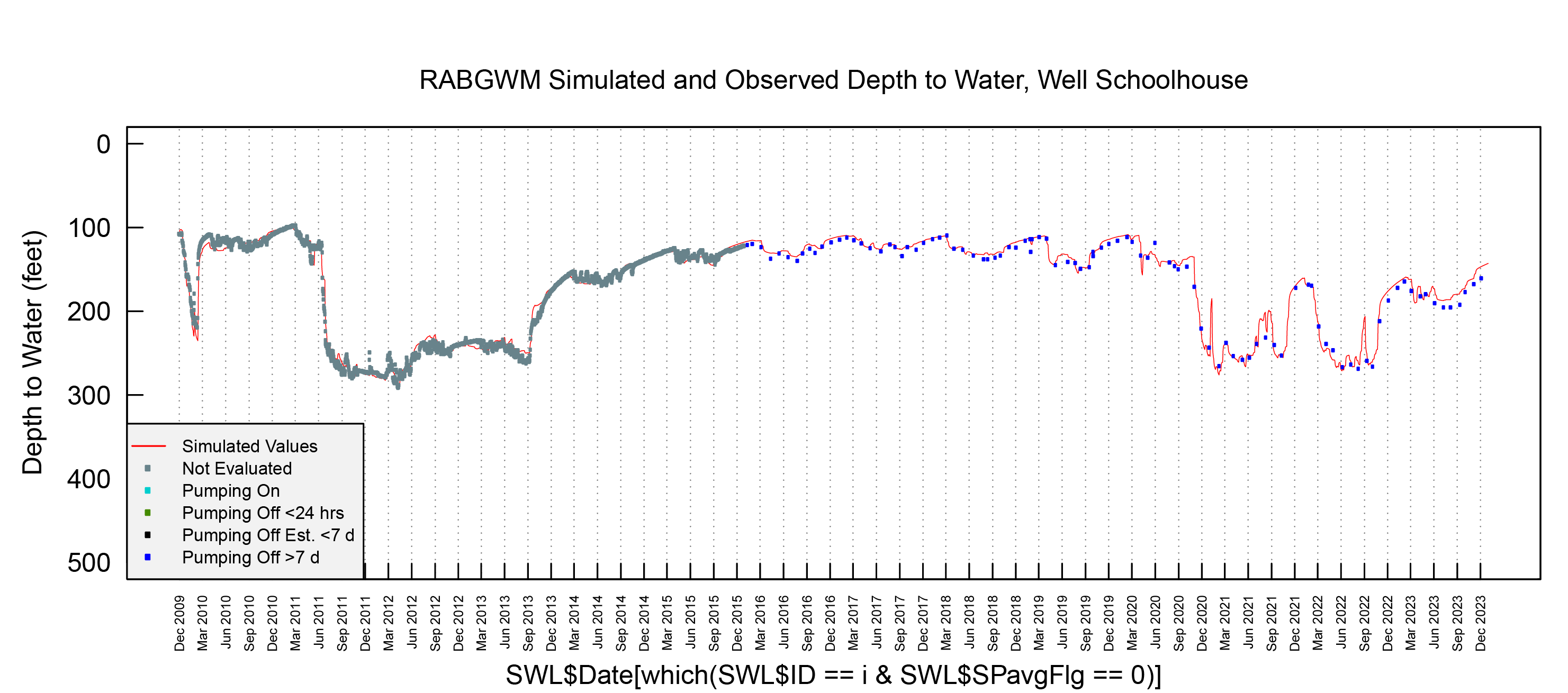
A critical step in many model applications prior to providing decision support is calibration and uncertainty analysis. Calibration can yield understanding of how well a model reflects reality; uncertainty analysis can identify variables that most significantly impact decision making and help guide data acquisition to reduce uncertainty. SSP&A has developed calibration and uncertainty analysis methods and software; teaches professional courses on these topics; and routinely calibrates and performs uncertainty analyses on models developed in-house and models developed by others. Our modeling experts assist clients with a multitude of applications, including:
- Conjunctive water resource evaluation and management;
- Contaminant fate and transport;
- Remedy design for water, soil, and soil vapor;
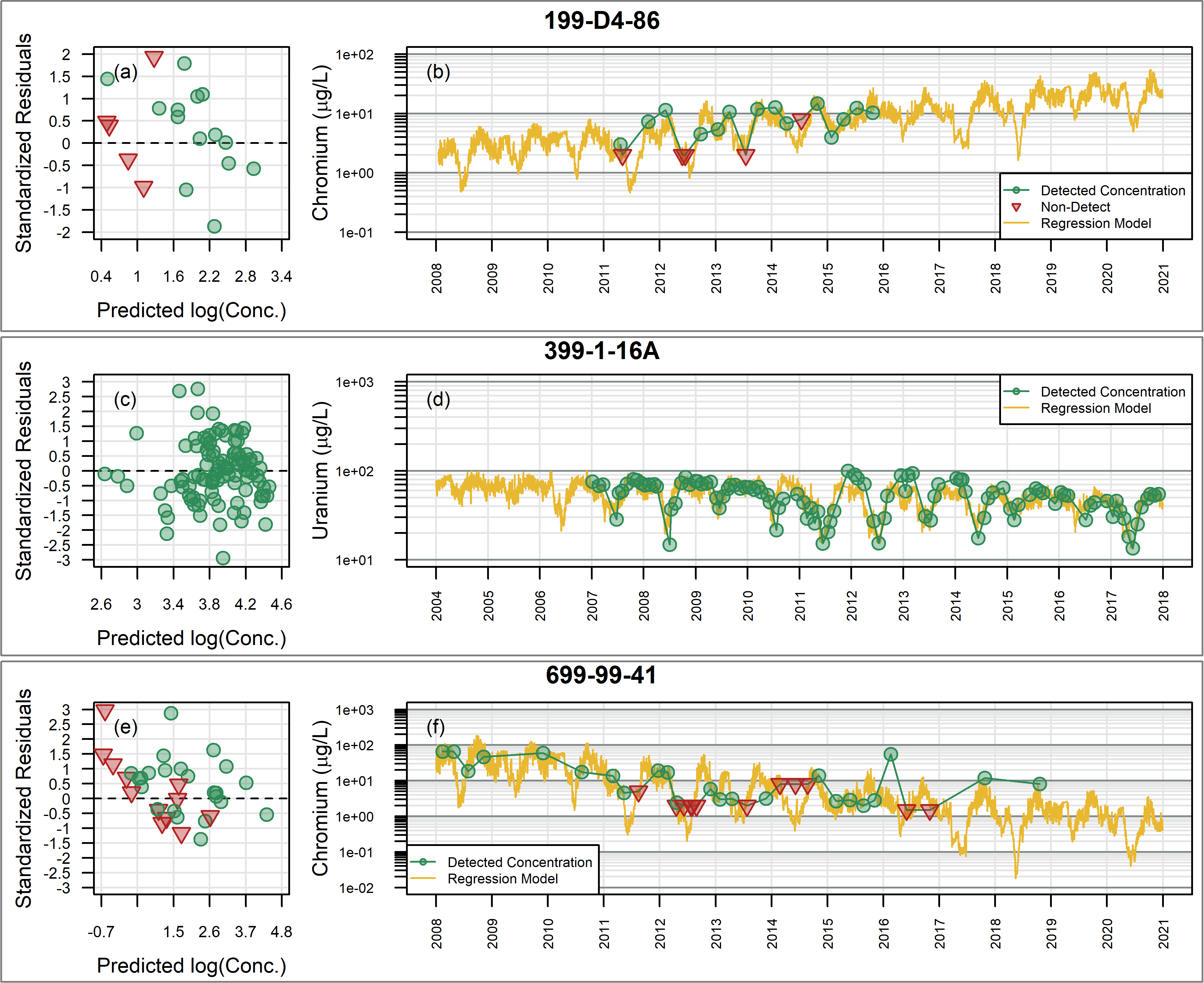
- Occurrence, fate, and treatment of natural contaminants (e.g., arsenic and chromium);
- Aquifer storage and recovery (ASR);
- Managed aquifer recharge (MAR);
- Analysis of indirect potable reuse (IPR);
- Modeling the sources of elevated total dissolved solids (TDS); and
- Geochemical characterization, formulation, and modeling using PHREEQC.
Conjunctive-Use Management of Groundwater and Surface Water
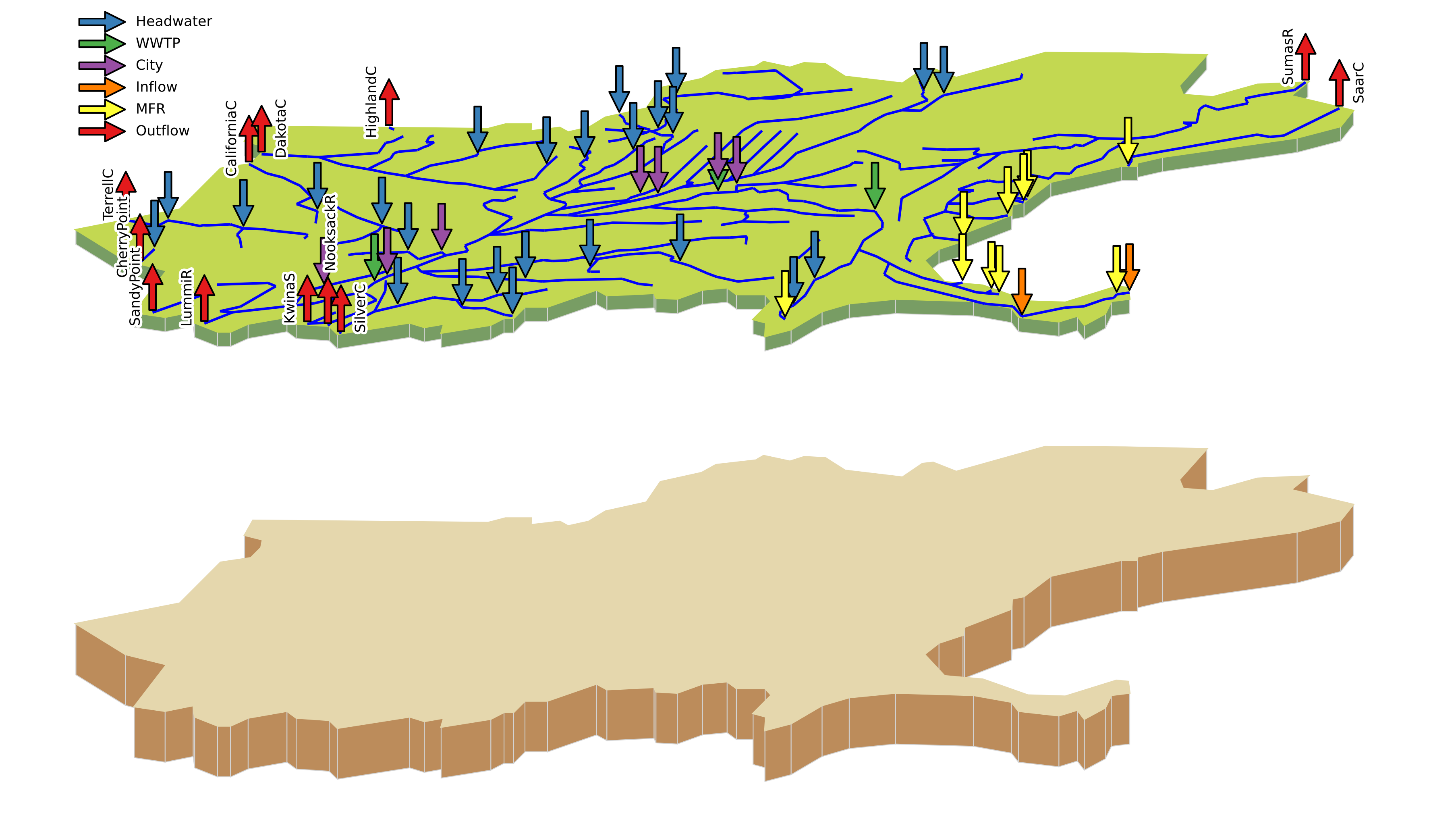
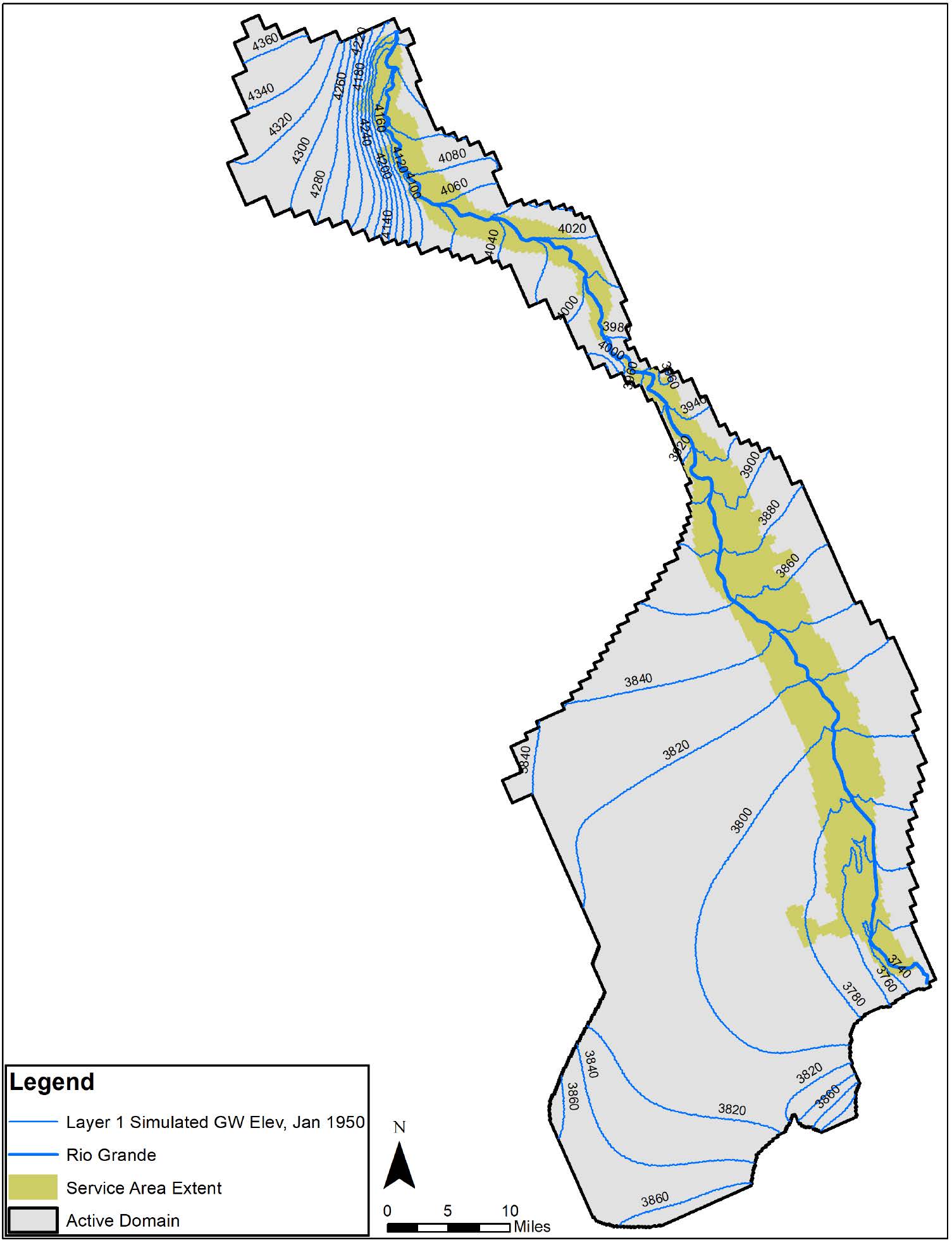
To assist clients in managing and utilizing available water supply resources, particularly in regions experiencing drought, SSP&A conducts modeling to assess the interaction of groundwater and surface water from rivers, streams, ponds, and wetlands. SSP&A evaluates water sources and supplies available for basin recharge; the capacity of specific aquifers to store recharged water; drawdown and stream depletion impacts of pumping stored water; and model suitability for forecasting hydrologic conditions in groundwater basins. Our services include:
- HCM development;
- Technical review of proposed conjunctive use plans;
- Source water characterization;
- River route and groundwater model coupling; and
- Injection/recharge facility design recommendations and construction oversight.
For these types of modeling applications, SSP&A has applied widely-available simulators such as variants of the MODFLOW family of codes, together with extended capabilities brought by GSFLOW and other packages; and numerous other simulators in both off-the-shelf and custom applications, including the California Department of Water Resources (CA-DWR) Integrated Water Flow Model (IWFM); the integrated surface-subsurface simulator ParFlow-CLM; the river network and management simulator RiverWare; and numerous land surface process and soil moisture balance simulators including INFIL, HYDRUS, DPWM, SWB, and SWAT.
Tikhonov Regularization Interpolation Method (TRIM)
TRIM – For challenging settings that require water-level mapping and pathline analysis, SSP&A developed a hybrid method for interpreting water-level data using a highly-parameterized unstructured MODFLOW-USG grid and regularized inversion, referred to as the Tikhonov Regularization Interpolation Method or TRIM.
Modeling in Support of ASR, MAR and IPR Evaluations and Facilities
With the increasing scarcity of available or economically accessible freshwater supplies, increasing attention has been paid to identifying alternative supplies and improved management of available supplies. ASR, MAR, and IPR are the three common frameworks that exhibit overlap in their technologies, environmental considerations, and simulation requirements.
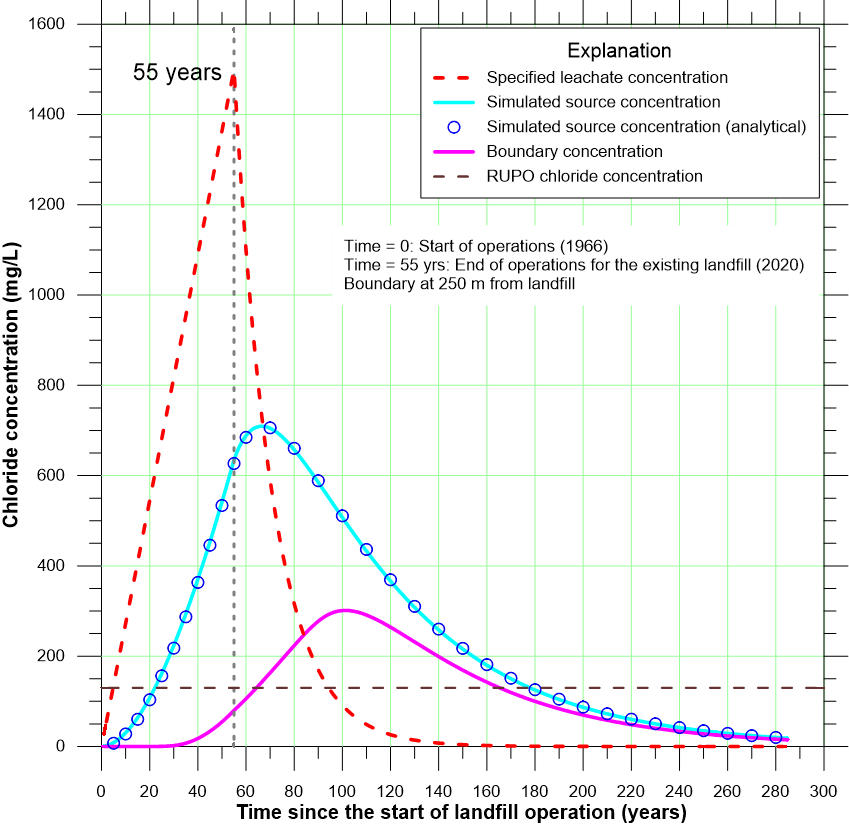
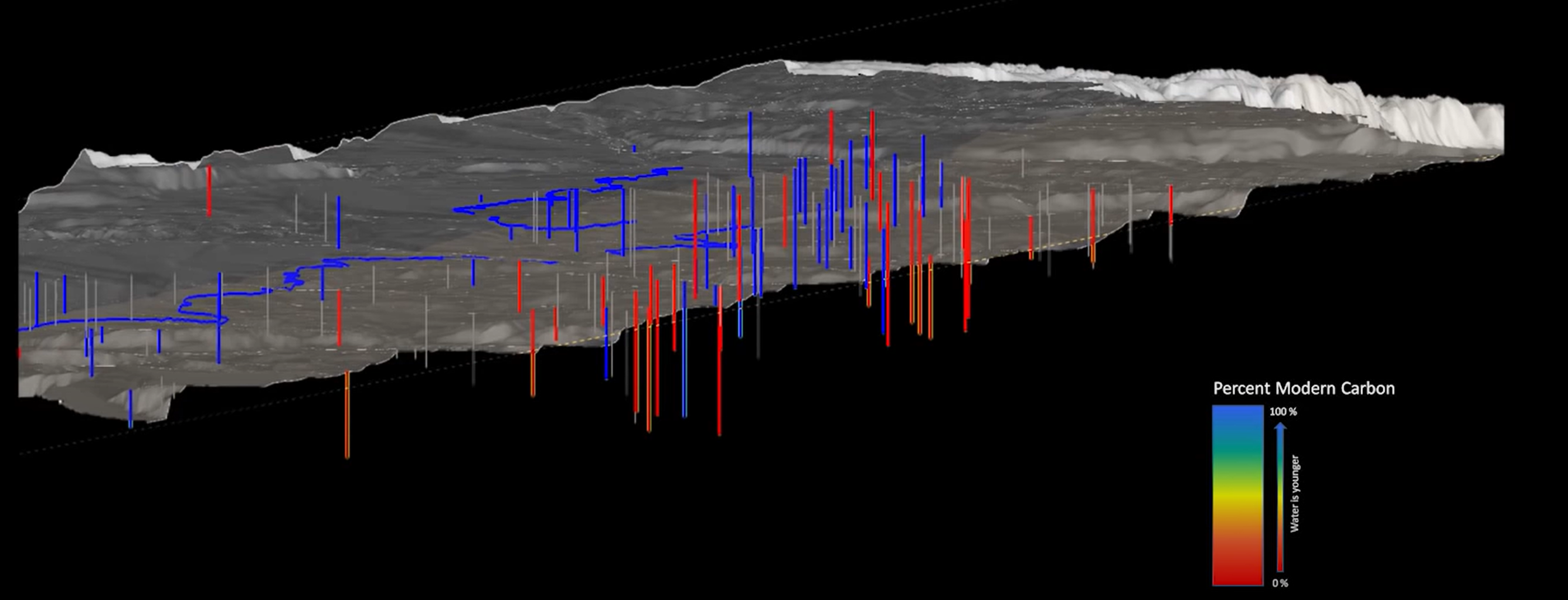
Contaminant Fate and Transport
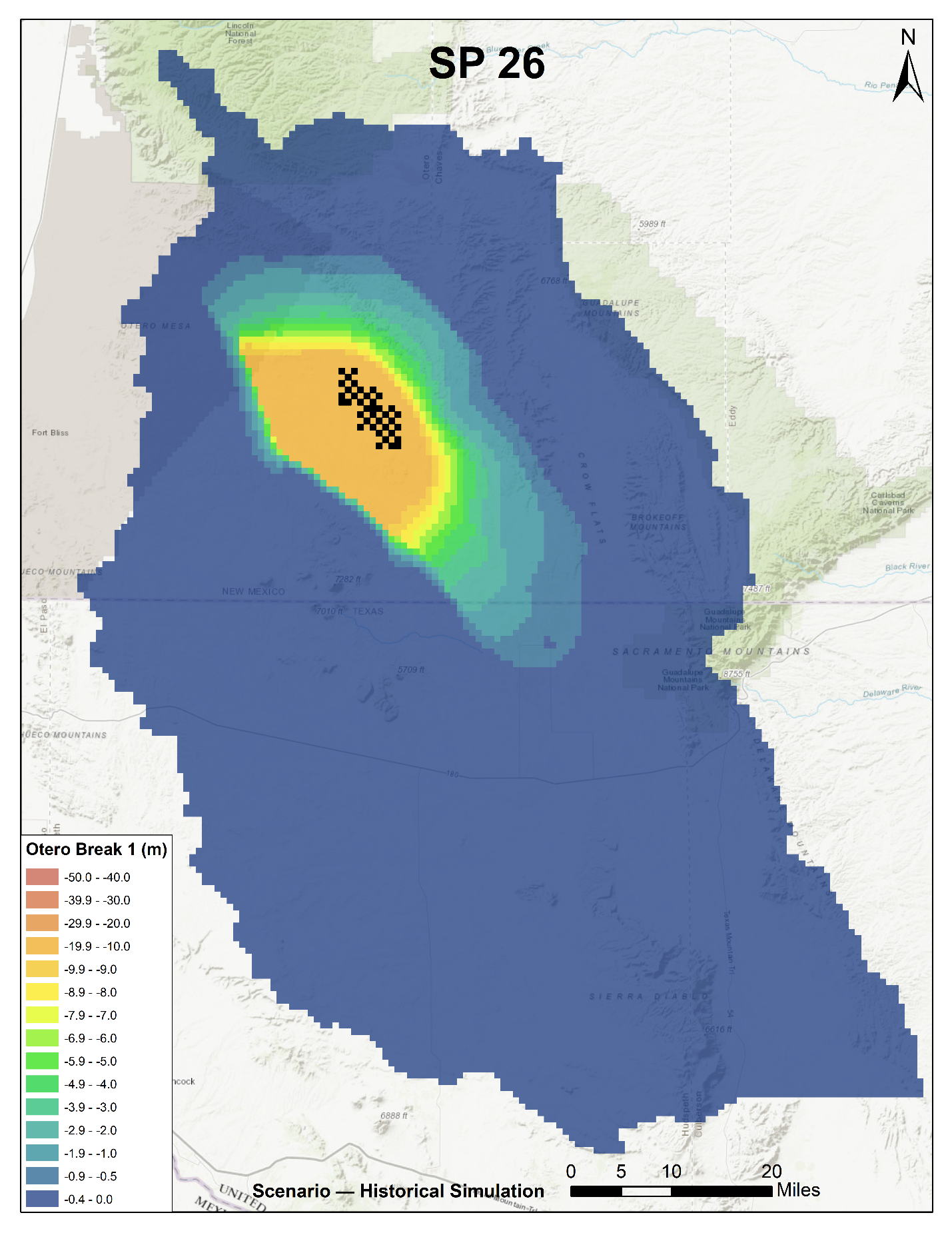
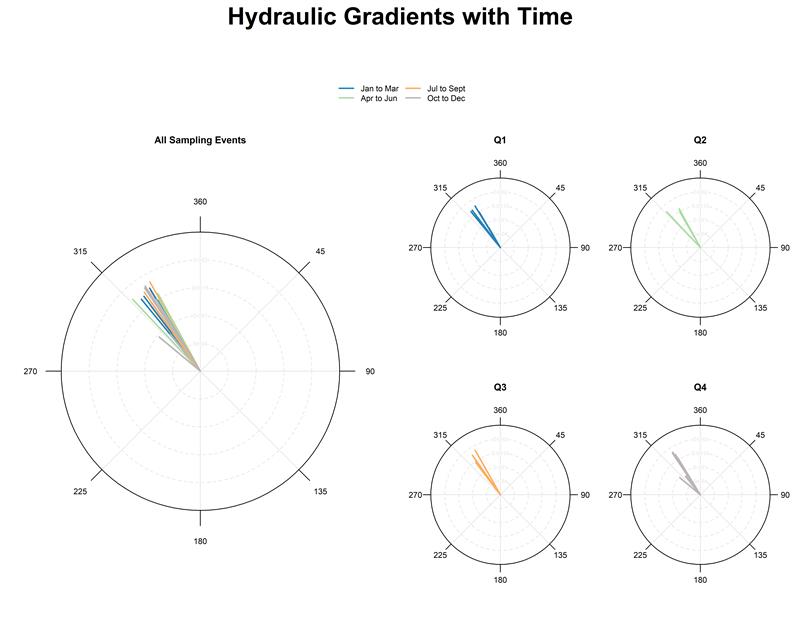
Analysis of the source locations and source history, migration and fate, and ultimately the risk posed by environmental contamination often rests on the development of models of contaminant fate and transport. The sophistication of these models can range from one-dimensional (1D) analytical solutions that assume a single species and homogeneous isotropic conditions to transient, heterogeneous, three-dimensional (3D) models of multiple interacting species. Determining which of the wide range of methods and codes is appropriate for site-specific analyses requires a comprehensive understanding of both the available methods and codes, and of the underlying theory.
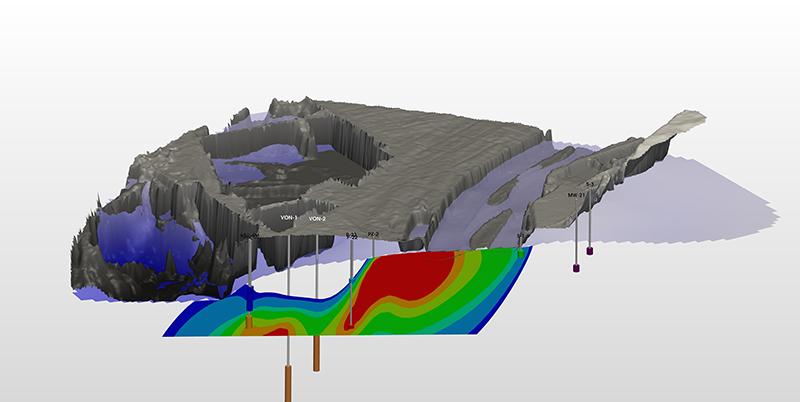
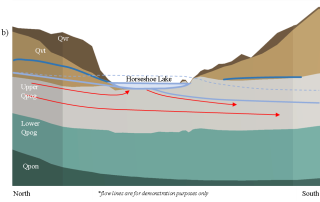
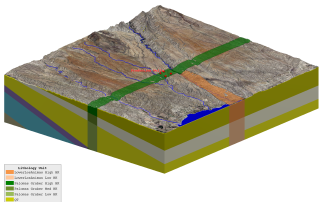
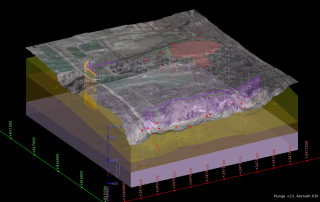
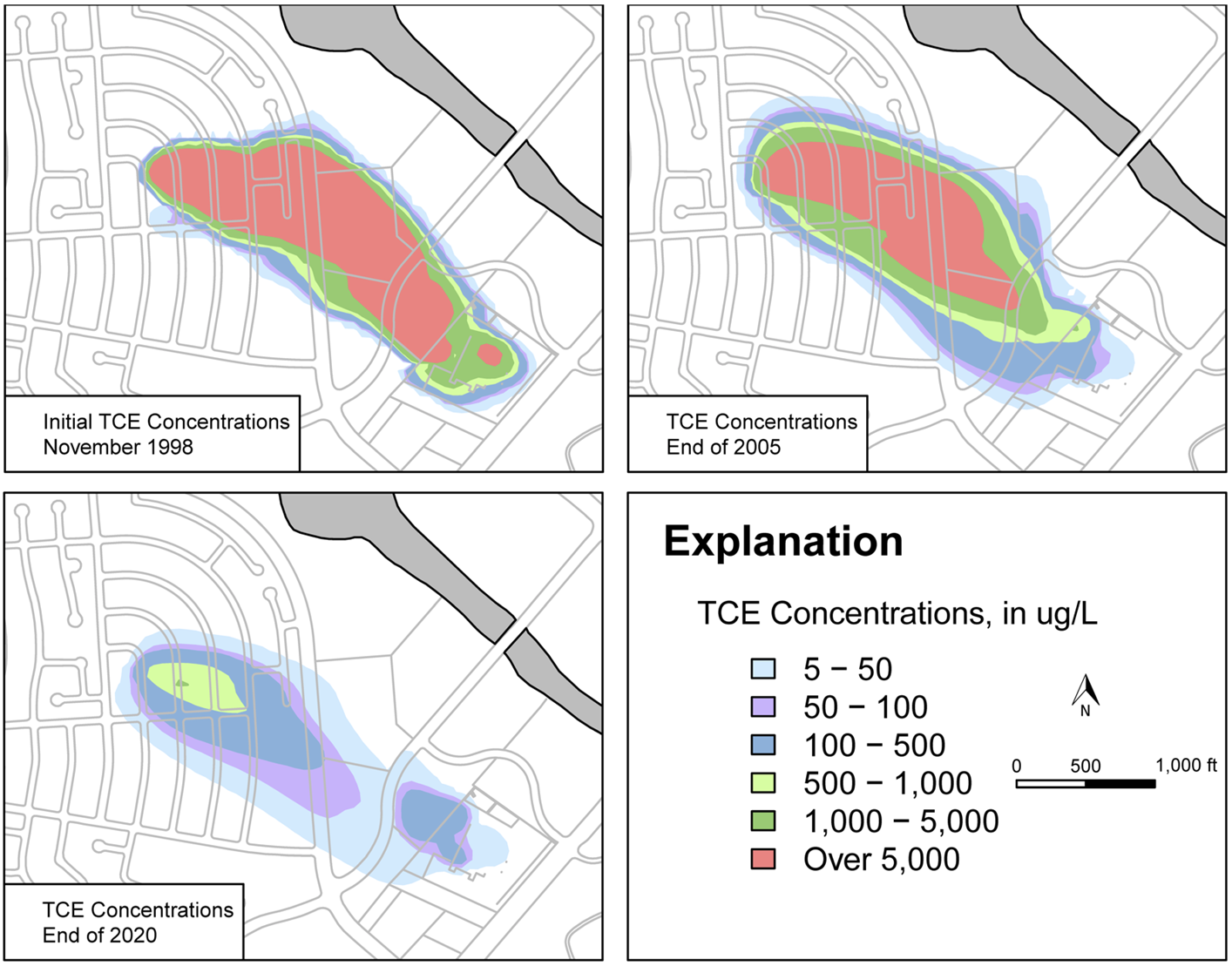
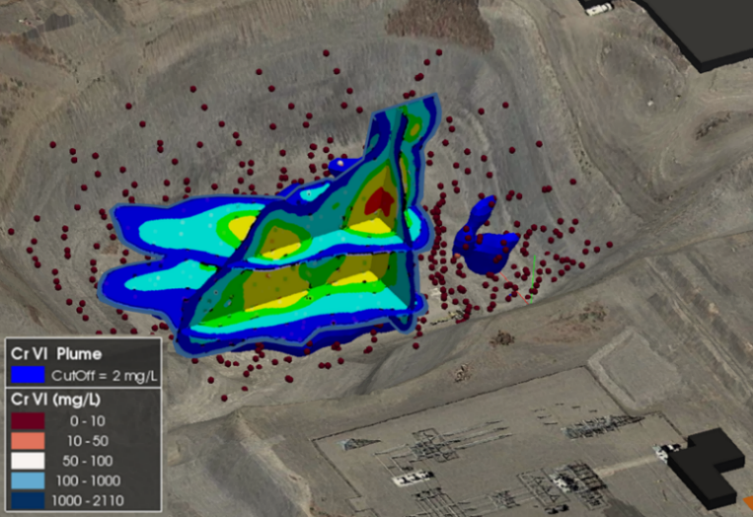
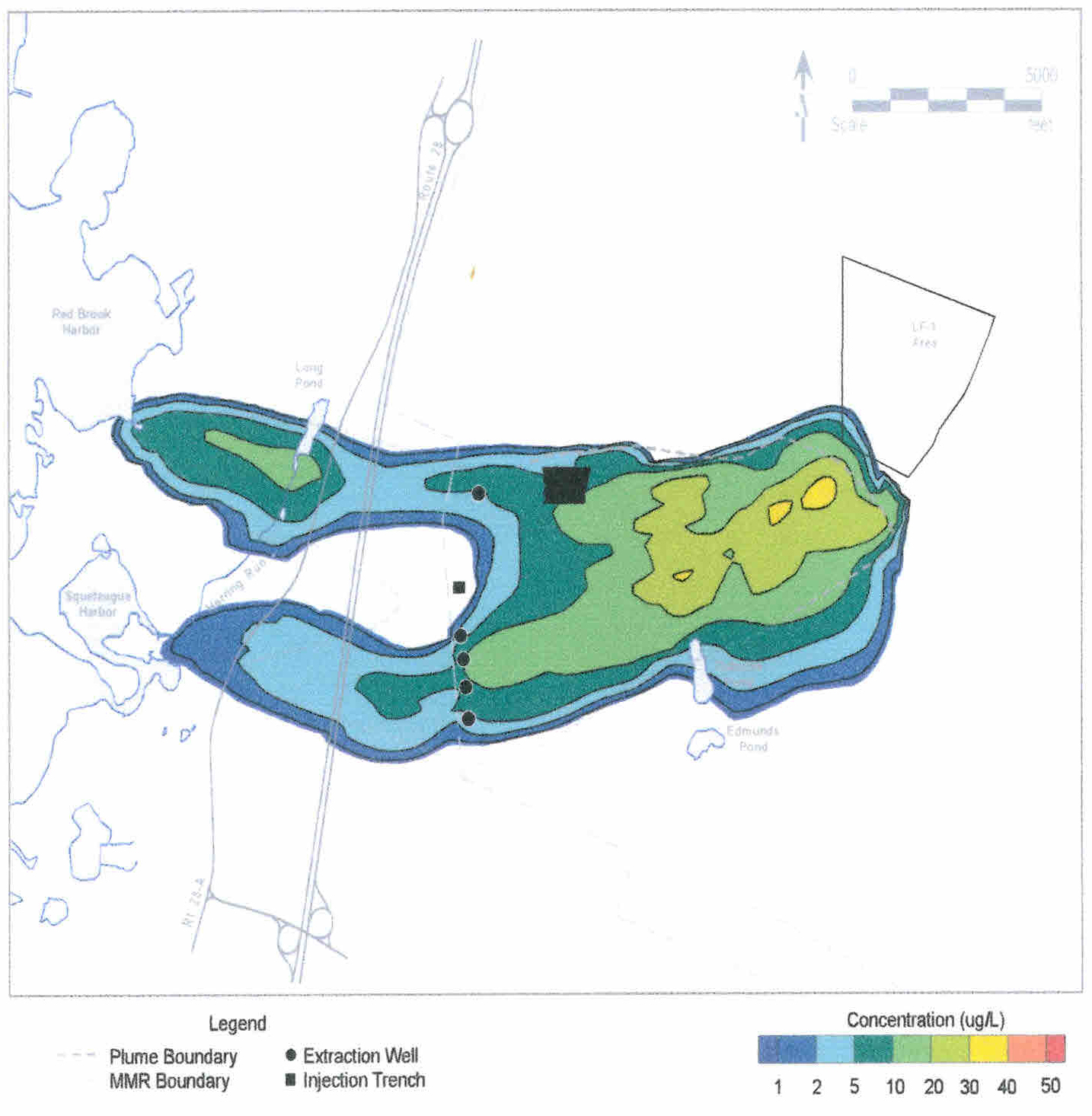
Mapping Contaminant Fate and Transport
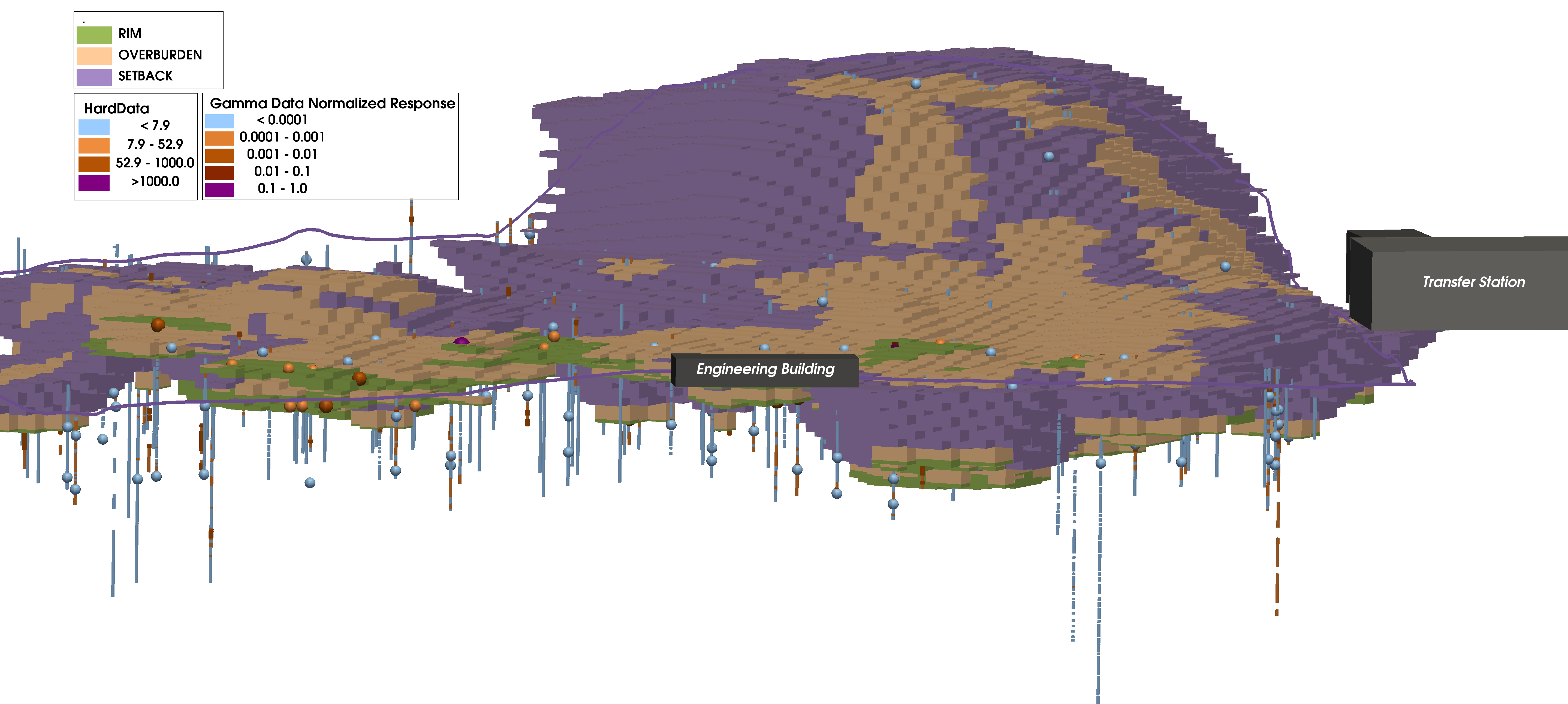
Interpolated groundwater elevation map under a quarry, with surface topography (DEM), cross-section of interpolated 3D contaminant plume, and locations of key wells.
Modeling for Remedy Design for Water, Sediments, and Soil Vapor
With the unique combination of disciplines collected under one (virtual) roof, SSP&A is ideally positioned to provide end-to-end client support for the design, monitoring, performance evaluation, optimization, attainment demonstration, and closure of remedies for environmental media. SSP&A applies physics-based and (geo-)statistical models to support remedy designs, including:
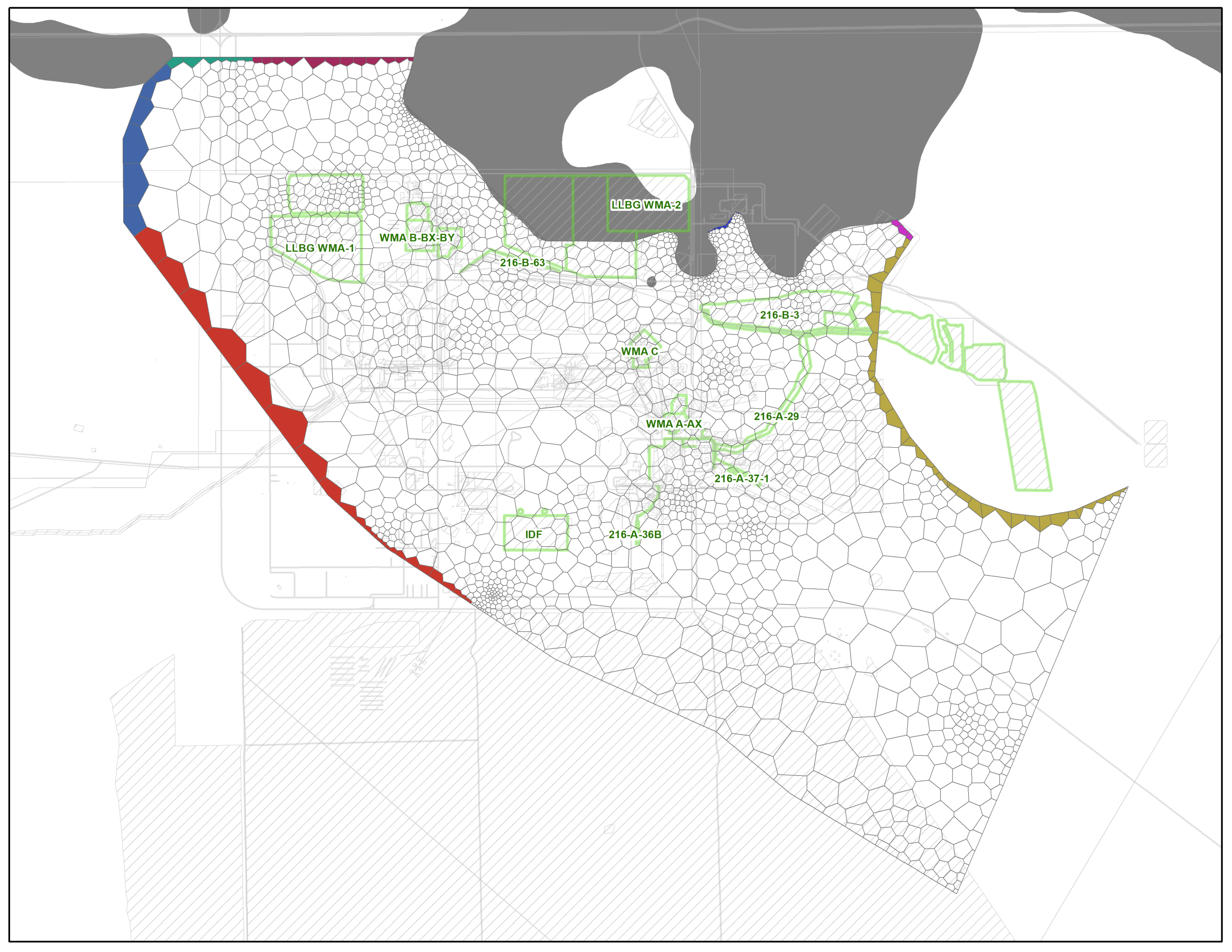
- Multiple-indicator geostatistical analysis of radionuclides in landfill waste to optimize partial excavation remedies;
- Multi-phase fate-and-transport analysis for air-sparge/soil vapor extraction (AS/SVE) remedies of fuel-related contaminants including MTBE;
- Multi-component analysis of groundwater pump-and-treat (P&T) remedies including optimization of extraction and injection locations and rates, and optimal design of the treatment train using the Contaminant Treatment System (CTS) package originally developed at SSP&A on behalf of the U.S. Department of Energy (USDOE); and
- Simulation of in-situ chemical amendments and other enhancements for the treatment of hexavalent chromium (CrVI), arsenic (As), chlorinated solvents (CVOCs), and petroleum-derived contaminants.
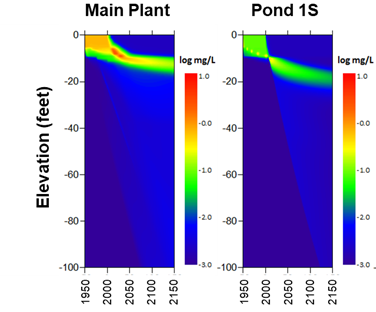
Modeling the Sources of Elevated Total Dissolved Solids
Poor quality groundwater, in terms of elevated TDS for example, can arise from a combination of complex natural and anthropogenic causes including seawater intrusion and up-coning; water that is co-produced during certain terrestrial oil recovery activities (“produced water”); brackish water occurring within certain geological formations; and deep brackish water which was emplaced in the subsurface centuries or millennia ago, and may include “connate” water that was trapped in sediments as they were deposited. Through our combination of modeling and geochemical expertise, SSP&A has developed numerous models for forensic determination of the relative contribution to targeted aquifers of these various natural and man-made sources of poor-quality water.
Geochemical Characterization, Formulation, and Modeling using PHREEQC
SSP&A’s technical expertise allows us to modify and enhance the transport capabilities that are available in the most widely used groundwater modeling codes. Our capabilities in multiple disciplines – groundwater modeling (e.g., MT3D-USGS and MODFLOW-USG), geochemical modeling (e.g., PHREEQC, Geochemist’s Workbench), multi-language code development, and quantitative methods – enable SSP&A to identify, interpret, formulate, program (i.e., develop code), and implement novel reactive transport procedures.
Beyond the application of models, SSP&A provides leadership in modeling techniques and software development. We developed the and continue to support the most widely-used solute transport simulator in the world, MT3D, with the most recent version released in collaboration with the U.S. Geological Survey.
SSP&A also wrote the book on solute transport simulation: Applied Contaminant Transport Modeling – Theory & Practice.
SSP&A is often retained to perform model calibration and uncertainty analysis for clients who have already developed models and are looking to understand the level of confidence they can have in their model, or to determine if their model needs to be updated.